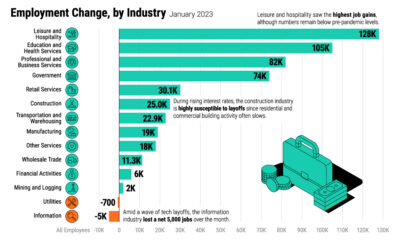
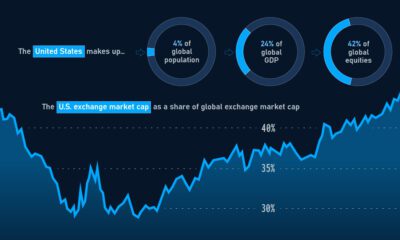
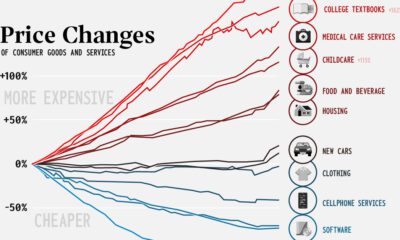
The United States is a vast place, and every region is markedly different. Usually we look at these differences through lenses like geography, population density, preferences, wealth, and culture – but age is another interesting one to think about, and age is a significant factor in predicting future economic health and growth for almost any society.
The Age Factor
As the French philosopher Auguste Comte wrote, “Demography is destiny”. If you know a person’s age, you’re usually able to guess other things about them. For example, younger people are usually more motivated and inclined to launch careers, start families, and seek economic security. Not all young people are this way of course – but in aggregate, this is generally true. Today’s map comes to us from Reddit user /r/JFBoyy and it charts median age by every U.S. county, parish, borough, and Census Area.
Counties by Age
Which states and counties stand out on the map? Utah is an interesting place to start – it’s the youngest state with a median age of 29.9, and this is extremely clear when looking at the county level. The state has only one county (Daggett) with a median age range above 35-44 years. Florida and Maine are two other states that stand out. Florida is the stereotypical “old” state, and there is some truth to that based on the numbers. It’s the only state that has a county (Sumter) with a median age range over 65 years. Meanwhile, Maine has only five counties that are not “old” counties – and the majority of counties have median ages that fall in the 45-54 range. The Midwest and Southeast seem to have a higher distribution of counties with median ages in the “middle ground” 35-44 median age range. Alabama has 67 counties, and all but five of them are in that bracket. Meanwhile, the West seems to have an interesting dichotomy in many of its states. Washington State, for example, has many counties with old populations (San Juan, Jefferson, and others) but also counties with younger populations (Whitman, Yakima, Kittitas). Idaho is the most potent example of this tendency: all of the old people seem to live in the north of the state, and all of the young people in the south.
A Look to the Future
Here is how median age projects out to 2040, but on a state level.
Overall the national median age is projected to go from 37.7 to 39 years. Interestingly, while aging in the United States is expected to cause some demographic issues in the long run, the country’s challenges pale in comparison to other rapidly-aging countries in the Western world. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.