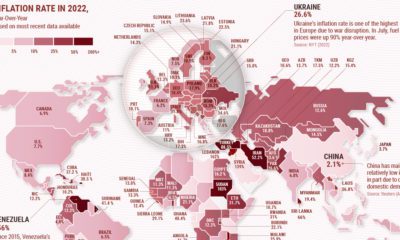
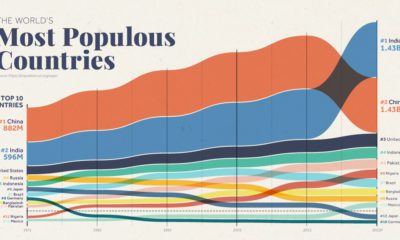
The visualization above looks to give people a different frame of reference to think about the country’s massive population figures.
The Population Breakdown
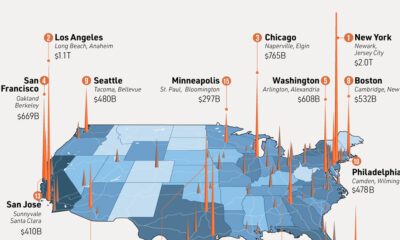
Similar to other big countries, the gap between India’s largest and smallest states is quite wide. Uttar Pradesh is the most populous country subdivision in the world at 232 million people, while Sikkim, in the northeast of the country, is the least populated state in India (0.7 million). Here are India’s 28 states and 8 union territories compared to other countries and territories with comparable sizes: Hypothetically, if India’s states were to all became countries today, they would take up half the spots in a ranking of the world’s top 20 most populous countries. A number of Indian states match up evenly against some very large countries, including Maharashtra (Japan), West Bengal (Egypt), and Tamil Nadu (Germany). Of course, the largest is Uttar Pradesh (Brazil+Chile), which also happens to measure up to neighboring Pakistan. For people living in countries such as Canada or Australia, it may be humbling to know that these countries are equal to a smallish Indian state.
The Big Get Bigger
According to United Nations projections, India is on track to become the most populous country in the world in 2023. The population of India’s growth is fueled by several factors, including declining mortality rates, increased life expectancy, and high birth rates. While India’s population growth has slowed in recent years due to factors such as urbanization and increasing access to contraception, the country’s population is still expected to continue growing at a significant rate for the foreseeable future. Source: Population projections for India are from indiacensus.net. Population figures for comparison countries are from the UN’s World Population Prospects: The 2019 Revision (medium-fertility variant), accessed via Worldometers‘ live tracker. All population figures shown are 2022 projections. Data note: Because there are only so many countries, the populations of comparison countries may not perfectly match that of the various Indian states and union territories. Numbers are rounded. Map note: A number of borders and regions in India are disputed with other countries. Our depiction of borders is a good faith, apolitical attempt at reflecting the “de facto” situation in each region. on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.