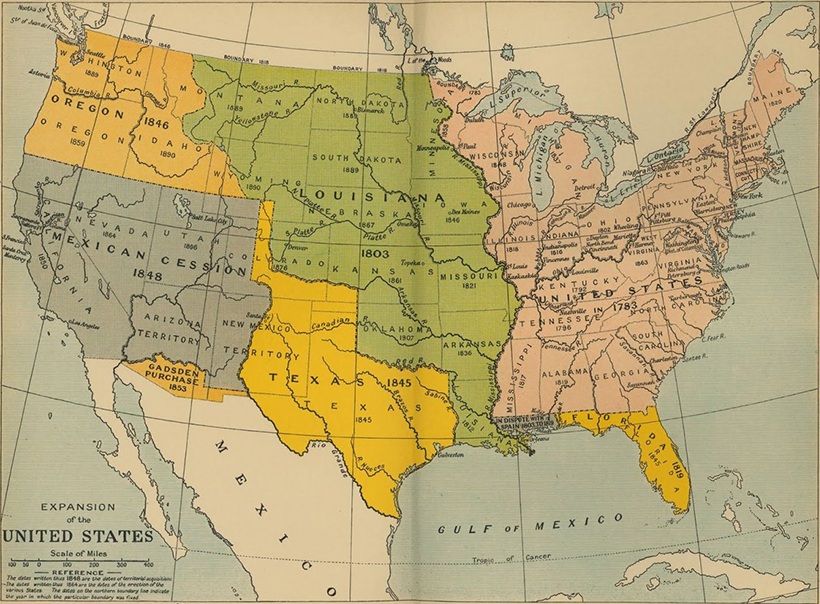
The United States is the third largest country in the world, with a vast territory extending beyond the borders of the contiguous states. To be exact, the United States is made up of 50 states, nine uninhabited territories, five self-governing territories, one incorporated territory, and one federal district (Washington D.C.). The boundaries of the country haven’t changed much in recent years, but the lines on the map have shifted numerous times in history, through both negotiation and bloodshed. Today’s above animation, by u/Golbwiki, is the perfect visual aid to understand how the United States evolved from the Thirteen Colonies to its current form. Here are five of the largest expansion events in U.S. history.
1803: Louisiana Purchase
Napoléon Bonaparte didn’t just have a huge impact on Europe, he also altered the course of history in the New World as well. The French General was waging an expensive war in Europe, and began to view the Louisiana Territory as a burden – as well as a potential source of income. In 1803, he offered up all 828,000 square miles for the famously low price of $15 million. This massive land purchase comprises nearly 25% of the current territory of the United States, stretching from New Orleans all the way up to Montana and North Dakota.
1819: Adams–Onís Treaty
Spanish explorers first established a presence in Florida as far back as 1565, but 250 years later, Spain had done little to cement its foothold in the region. The Spanish realized they were in poor position to defend Florida should the U.S. decide to seize it. In 1819, Secretary of State John Quincy Adams negotiated the signing of the Florida Purchase Treaty, which officially transferred Florida to the United States after years of negotiations. There was no official cost of purchase, but the U.S. government agreed to assume approximately $5 million of claims by U.S. citizens against Spain.
1845: Texas Annexation
The newly created Republic of Texas, which broke away from Mexico in the Texas Revolution, was peacefully annexed by the United States in 1845. In one fell swoop, the U.S. acquired 389,000 square miles of former Mexican territory.
1848: Mexican Cession
Shortly after the Texas Annexation, tensions between Mexico and the U.S. flared up anew. Congress declared war on Mexico over a boundary dispute in 1846, and after a relatively brief armed conflict – known as the Mexican–American War – the two countries signed the Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo. The treaty recognized Texas as a U.S. state, and the United States took control of a huge parcel of land that includes the present-day states of California, Nevada, and Utah, as well as portions of Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, and Wyoming. Mexico received $15 million in the arrangement, but saw the size of their territory halved.
1867: Alaska Purchase
In the aftermath of the Crimean War, Alexander II began exploring the possibility of selling Alaska. Similar to Spain’s foothold in Florida earlier in the century, the Russian Emperor recognized the possibility of American incursions into the territory, which they were not in a good position to defend against. – Grand Duke Konstantin of Russia After an all-night negotiation session on March 30, 1867, Alaska was sold to the United States for $7.2 million – the equivalent of $109 million in 2018. Alaska officially became a state in 1959.
Scratching the Surface
The examples above are only a brief overview of the complex evolution of shifting territorial claims in America. For those who want to take a deep dive into the shifting borders of America, here is an extremely thorough animation, also by the same author:
Of course, colonial expansion in North America didn’t occur in a vacuum. For an Native American perspective on this topic, check out this animated map. on Cities—settlements that are densely populated and self-administered—require many specific prerequisites to come into existence. The most crucial, especially for much of human history, is an abundance of food. Surplus food production leads to denser populations and allows for people to specialize in other skills that are not associated with basic human survival. But that also means that cities usually consume more primary goods than they produce. And their size requires a host of many other services—such as transport and sanitation—that are traditionally expensive to maintain. So maintaining large urban centers, and especially the world’s largest cities, was a monumental task. Mapper and history YouTuber Ollie Bye has visualized the seven largest cities in the world since 3,000 BCE. His video covers cities with a minimum population of 10,000 and hints at historical events which led to the establishment, growth, and eventual fall of cities.
The World’s Largest City Throughout History
With any historical data, accuracy is always a concern, and urban populations were rough and infrequent estimates up until the Industrial Revolution. Bye has used a variety of data sources—including the UN and many research papers—to create the dataset used in the video. In some places he also had to rely on his own estimates and criteria to keep the data reasonable and consistent:
In early history, some cities didn’t have given population estimates for long periods of time, and had to be equalized or estimated through other sources. For example, Babylon had a population estimate at 1,600 BCE (60,000) and at 1,200 BCE (75,000) but none in the 400 years between. Cities that only briefly climbed above a population of 10,000, or that would have made the largest cities ranking for only a couple of years (and based on uncertain estimates), were not included.
Here’s a look at the largest city starting from the year 3,000 BCE, with populations listed in millions during the last year of each city’s “reign.” Cities are also listed with the flags of current-day countries in the same location.
Ancient Cities in the Fertile Crescent
Considered the “cradle of civilization,” the Fertile Crescent in the Middle East was home to all seven of the largest cities in the world in 3,000 BCE. The Sumerian city of Uruk (modern-day Iraq), allegedly home to the legendary king Gilgamesh, topped the list with 40,000 people. It was followed by Memphis (Egypt) with 20,000 inhabitants. For the next 1,700 years, other Mesopotamian cities in modern-day Iraq and Syria held pole positions, growing steadily and shuffling between themselves as the largest. 2,250 BCE marked the first time a different Asian city—Mohenjo-Daro (modern-day Pakistan) from the Indus Valley Civilization—found a spot at #4 with 40,000 people. The table below is a quick snapshot of the seven largest cities in the world for from 3,000 BCE to 200 CE. Again, populations are listed in millions. It wasn’t until 1,250 BCE that the top two spots were taken by cities in different regions: Pi-Ramesses (Egypt) and Yin (China), both with more than 100,000 residents. Egyptian cities would continue to be the most populous for the next millennium—briefly interrupted by Carthage and Babylon—until the start of the Common Era. By 30 CE, Alexandria was the largest city in the world, but the top 10 had representatives from the Middle East, Northern Africa, and Asia.
All Roads Lead to Rome
One city in Europe meanwhile, was also beginning to see steady growth—Rome. It took until halfway through the 3rd century C.E. for Rome to become the most populous city, followed closely still by Alexandria (Egypt). Meanwhile in Iraq, Ctesiphon, the capital of the Sasanian empire was growing rapidly. Towards the end of the 3rd century, the Roman empire was divided into two, with Constantinople becoming the new capital for the Eastern half. Consequently, it had outgrown Rome by 353 and become the world’s most populous city, and for the next few centuries would reclaim this title time and time again.
The Largest Cities Reach 1 Million
In the 9th century, Baghdad became the first city to have 1 million residents (though historians also estimate Rome and the Chinese city of Chang’an may have achieved that figure earlier). It would be nearly nine centuries until a city had one million inhabitants again, and Baghdad’s reign didn’t last long. By the 10th century, Bian, the capital of the Northern Song dynasty in China, had become the largest city in the world, with Baghdad suffering from relocations and shifting political power to other cities in the region. From the 12th century onwards, Mongol invasions in the Middle East and Central Asia severely limited population growth in the region. European cities too were ravaged in the 14th century, but by plagues instead of marauders. For the next few hundred years, Cairo (Egypt), Hangzhou (China), and Vijayanagara (India) would top the list until Beijing took (and mostly held onto) the top spot through the 19th century.
Industrial Revolution and Rapid Urbanization
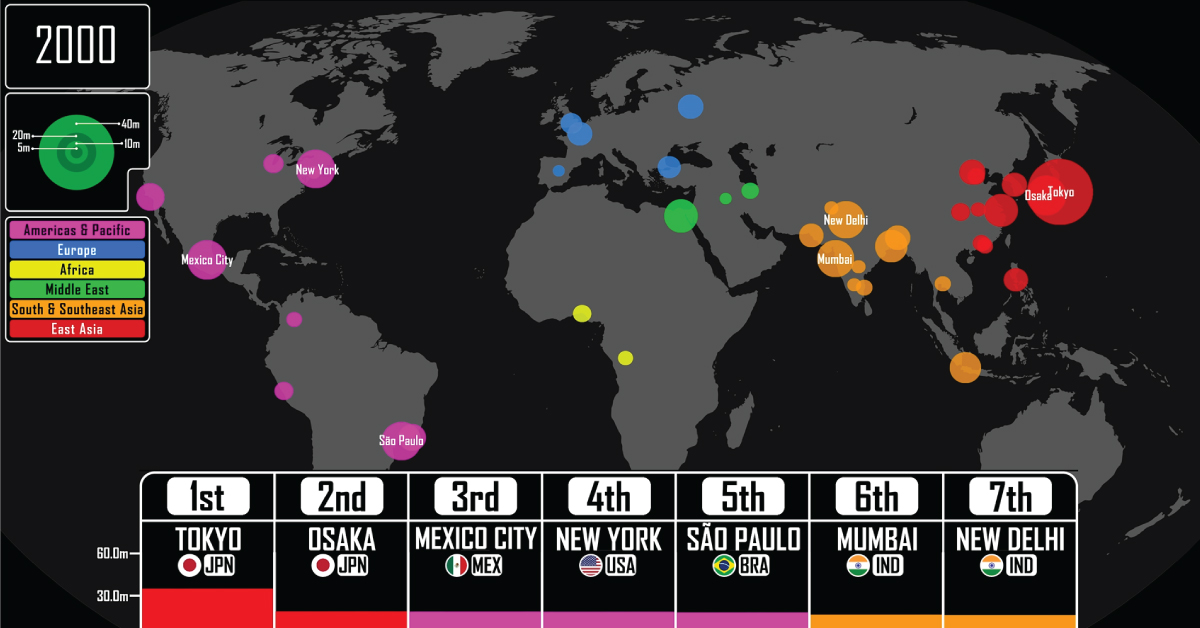
The start of the Industrial Revolution in the UK—spreading to the rest of Europe and later on the U.S.—led to hitherto unseen levels of urban population growth. Factories needed labor, which caused mass emigration from the rural countryside to urban centers of growth. In 1827, London passed Beijing to become the largest city in the world with 1.3 million residents. Over the next 100 years, its population increased nearly 7 times, remaining the most populous city until the end of World War I, by which time it was overtaken by New York. From 1920 to 2022, the world population quadrupled thanks to improvements in farming and healthcare, and cities saw rapid growth as well. The beginning of the 20st century saw the top 10 largest cities in the world in the U.S., Europe, and Japan. By the 21st century however, growth shifted away to other parts of the world and by 2021, the top seven had cities only from Asia and the Americas. Tokyo, which took the top spot in 1954, is the largest city in the world today with a population of 37 million (including the entire metropolitan area). It is followed by New Delhi with 31 million, but by 2028, the UN estimates that positions will switch on the leaderboard and New Delhi will overtake Tokyo.
What Does Population Growth Say About the Past (and Future)?
The rise and fall of cities through the sands of time can give us insight into the trajectory of civilization growth. As civilizations grow, become richer, and reach their zenith, so too do their cities blossom in tandem. For example, of the modern-day seven largest cities in the world, four of them belong to countries with the 10 largest economies in the world. Meanwhile, sudden falls in urban population point to turbulence—political instability, wars, natural disasters, or disease. Most recently Ukraine’s cities are seeing depopulation as residents flee conflict zones, raising the specter of a demographic crisis for the country should the war continue. Thus, tracking the size of urban population can help policymakers forecast future roadblocks to growth, especially when prioritizing sustainable growth for a country.